Bedwetting in Adults: Breaking the Silence on a Common Issue
Bedwetting in adults (medically referred to as nocturnal enuresis) may indeed be a sign of an underlying health condition. Bladder control issues rather at night can indeed be caused by an overactive bladder, urinary tract infection, or even sleep apnea.
Adult bedwetting needs to be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Finding the root cause of overnight accidents is of course essential for determining effective treatment.
Causes of Adult Bedwetting

Sleep Apnea Image
Nocturnal enuresis, or involuntarily urinating occurring during the nighttime, happens when the person’s bladder does not respond to signals that it needs to empty while sleeping. There are several possible reasons for this health issue:
Sleep Apnea
The sleep disorder which is referred to as sleep apnea does cause a person’s breathing to stop briefly while sleeping. These breathing interruptions tend to cause a drop in oxygen levels and can also affect bladder control.
Research does indicate that adults (and children) with sleep apnea can experience bedwetting.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is indeed a common infection that does affect the urinary system, which of course includes the kidneys, bladder, and urethra (the tube via which urine exits the body).
Notable UTI symptoms include an increased urge to urinate and also difficulty controlling urination. This can lead to involuntary bedwetting at night.
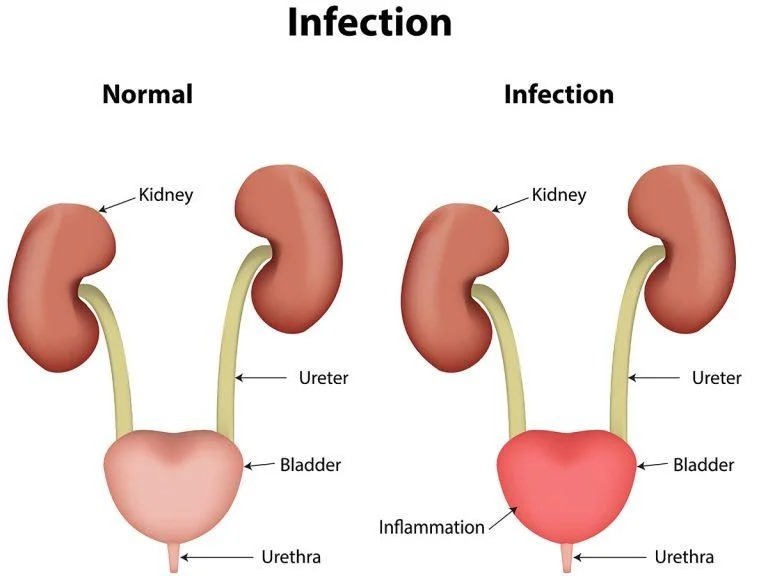
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Hormonal Issues
Issues with a certain hormone in one’s
body, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), can indeed also prompt adult bedwetting.
Overactive Bladder Muscles
Few people have overactive bladder muscles that contract involuntarily, even when there is not much urine in one’s bladder. This does lead to a sudden urge to urinate that can rather be difficult to control, which can result in nocturnal enuresis.
Small Bladder
Few people tend to have a smaller functional bladder capacity. Sometimes referred to as having a small bladder, the organ itself is not small, but rather it is able to hold less. This can of course result in bedwetting.
Diabetes
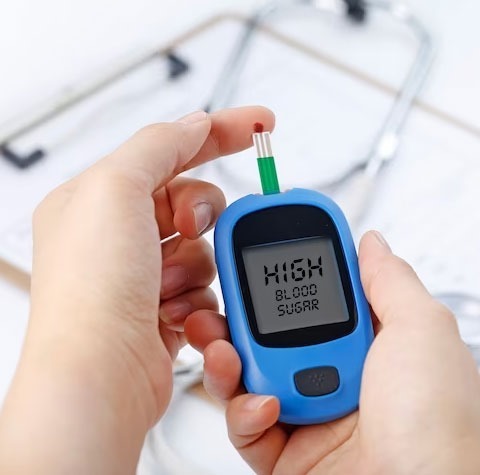
Diabetes
Undiagnosed or even poorly controlled diabetes can no doubt cause excessive production in a person’s urine. When it does occur during sleep, it is referred to as nocturnal polyuria. This can cause bedwetting.
Cancer
Bladder cancer and also prostate cancer are very potential underlying causes of nocturnal enuresis in adults.
Neurological Disorders
Several neurological diseases as well as disorders are linked to bedwetting in adults. Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, and even other neurological conditions can cause bladder control problems.
Lifestyle Factors
Few daily lifestyle habits do have the potential to affect one’s bladder or one’s sleep cycle, which could, in turn, prompt enuresis. Lifestyle factors like:
- Alcohol and caffeine consumption
- Sedatives or psychiatric medications
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress and anxiety
How Do You Stop Bedwetting?
A healthcare provider can in fact suggest a treatment plan for nocturnal enuresis that does work for a person.
Lifestyle Changes
A first course of treatment can include making a few behavioral, lifestyle, and habit changes, like:
- Stopping fluid intake late in the evening
- Avoid certain drinks such as caffeine or alcohol that increase the production of urine
- Learning bladder and also pelvic floor exercises (such as Kegels) to strengthen bladder muscles
- Wearing an adult pull-up diaper, if required in order to avoid an accident
- Practicing meditation techniques or even utilizing talk therapy to tackle stress reduction
Medication

caffeine
There is no doubt no specific medication that can “cure” bedwetting, there are a few options that may help decrease urine production during sleep or allow the bladder to hold more urine. Medications that are often used for this purpose include:
- Nocdurna (desmopressin acetate) mimics a body chemical that does control urine production.
- Chlorpheniramine in fact helps relax overactive bladder muscles
- Ditropan (oxybutynin) helps reduce or even stop bladder contractions while increasing the capacity of one’s bladder.
Surgery
If lifestyle tweaks and medication have not been successful, or if one’s case is severe enough, a surgical procedure can be considered.
Conclusion
Bedwetting in adults is worrisome and needs medical attention.





There are no comments