Difference between urticaria and urticaria pigmentosa
Urticaria is characterized by itchiness caused by weals or rather hives. Urticaria pigmentosa appears as a rash. Much difference is there between the two health conditions.
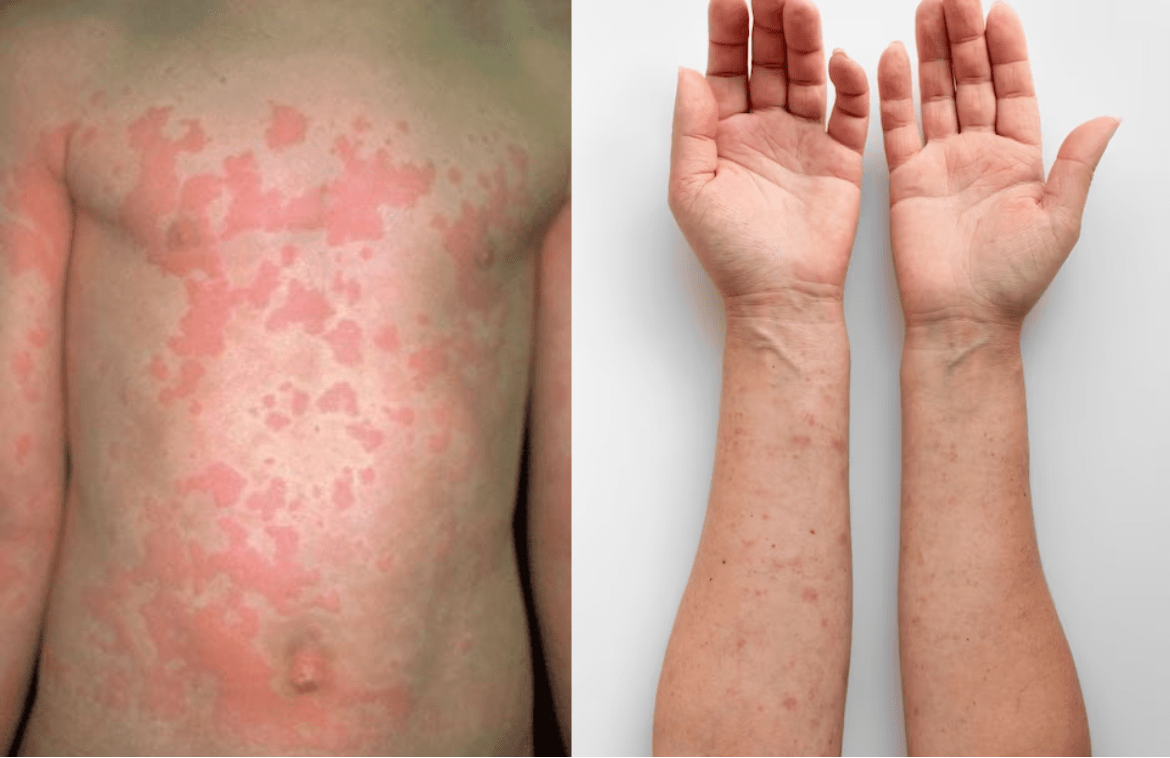
Urticaria happens to be characterized by very itchy weals (hives), with or without surrounding erythematous flares. The name urticaria is much derived from the common European stinging nettle Urtica dioica. Urticaria can indeed be acute or chronic, spontaneous or inducible. A weal (or wheal) is rather a superficial skin-colored or pale skin.
Urticaria tends to appear as raised, well-circumscribed areas of erythema (redness) as well as edema (swelling) involving the dermis as well as epidermis that is very pruritic (itchy), as shown in the image below. Acute urticaria can indeed be due to allergic reactions to foods, drugs, cosmetics, or perhaps soaps; infections; insect bites, stings, or exposure; environmental factors; latex; undue skin pressure, cold, or heat; emotional stress; as well as exercise, among other factors. It may be rather acute or chronic. Urticaria can be confused with a variety of other dermatologic diseases that happen to be similar in appearance and are also pruritic; usually, however, it can be distinguished from such diseases by an experienced clinician. Urticaria is of course not contagious unless the swollen hives contain a pathogen.
Urticaria (hives) happens to be a vascular reaction of the skin marked by the transient appearance of smooth and slightly elevated papules or even plaques (wheals) that are erythematous and that are often attended by severe pruritus. Individual lesions do resolve without scarring in several hours. Most cases of urticaria are self-limited and of short duration; the eruption rarely does last more than several days: yet, it can be recurrent over weeks. Chronic urticaria is defined as urticaria with recurrent episodes lasting longer than 6 weeks.
The development of urticaria is often an isolated event without systemic reaction. Rarely, it can be a prelude to the development of an anaphylactic reaction
Urticaria pigmentosa happens to be a rash that does appear most often in children as well as young adults. It does consist of reddish-brown lesions that can form hives or blisters when stroked. This reaction is known as Darier’s sign.
Urticaria pigmentosa is also considered to be a type of mastocytosis. This is when the mast cells happen to be part of one’s immune system build-up. Mastocytosis can indeed occur in a person’s skin, bones, intestines, or even other organs. Urticaria pigmentosa is when the build-up of mast cells tends to occur in the skin.
What is the difference between Urticaria and Urticaria pigemntosa?
The difference between the two conditions is of course whether the mast cells happen to be in the superficial dermis, which does result in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis as well as subcutaneous tissues, which does produce angioedema.
Diagnosis of urticaria pigmentosa
Is basal cell carcinoma (uncontrolled growths or lesions in one’s outer layer of skin) actinic keratosis (a precancerous scaly patch of skin caused by years of sun exposure). The doctor will indeed test any unusual-looking lesions for cancer. This will rather require a small skin sample for microscopic examination as well as testing. Wheal vs In the case of Urticaria the wheal happens to be a small raised swelling on the skin, often itchy, and of course caused by a blow from a whip or an insect bite, etc while urticaria is itchy, swollen, red areas of one’s skin which can appear quickly in response to an allergen or even due to other conditions.
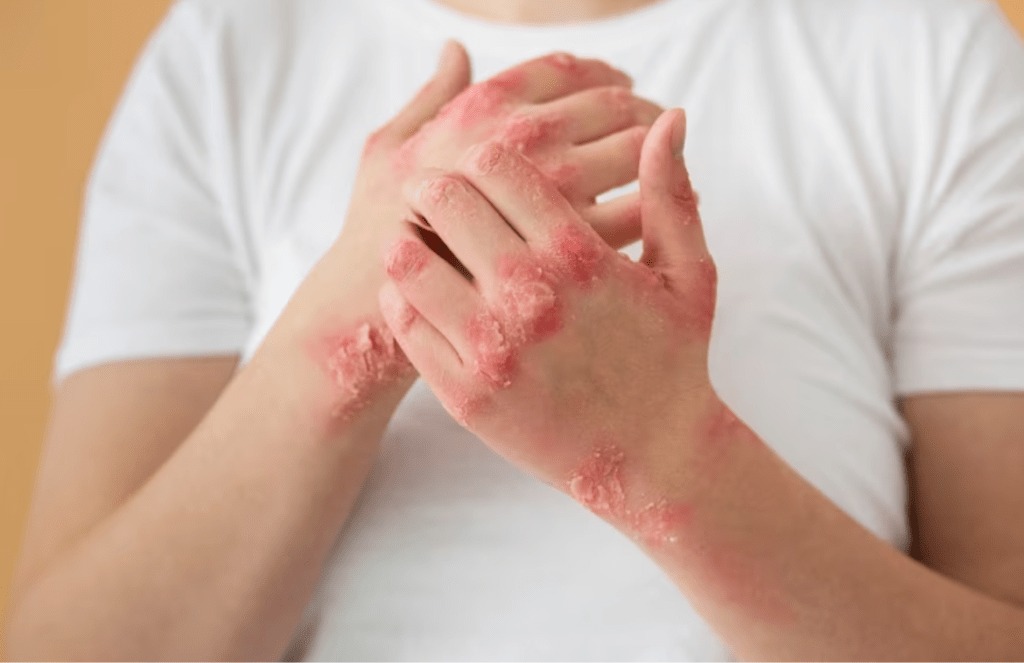

Insect bites do often result in itchy bumps (papules) or weals. Their characteristics do include
1. Initial sting is quite often felt.
2. On no doubt exposed sites.
3. Central blister (vesicle) is noticed.
4. Groups of lesions that are often distributed asymmetrically.
5. More commonly arise during summer and autumn months.
6. Individual lesions persist for days to weeks.
Conclusion
There is much difference between urticaria and urticaria pigmentosa.





There are no comments