The Six Secrets of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection is a health issue of much concern to both men and women more so for women. The causes of UTI are manifold and they need to be taken seriously.
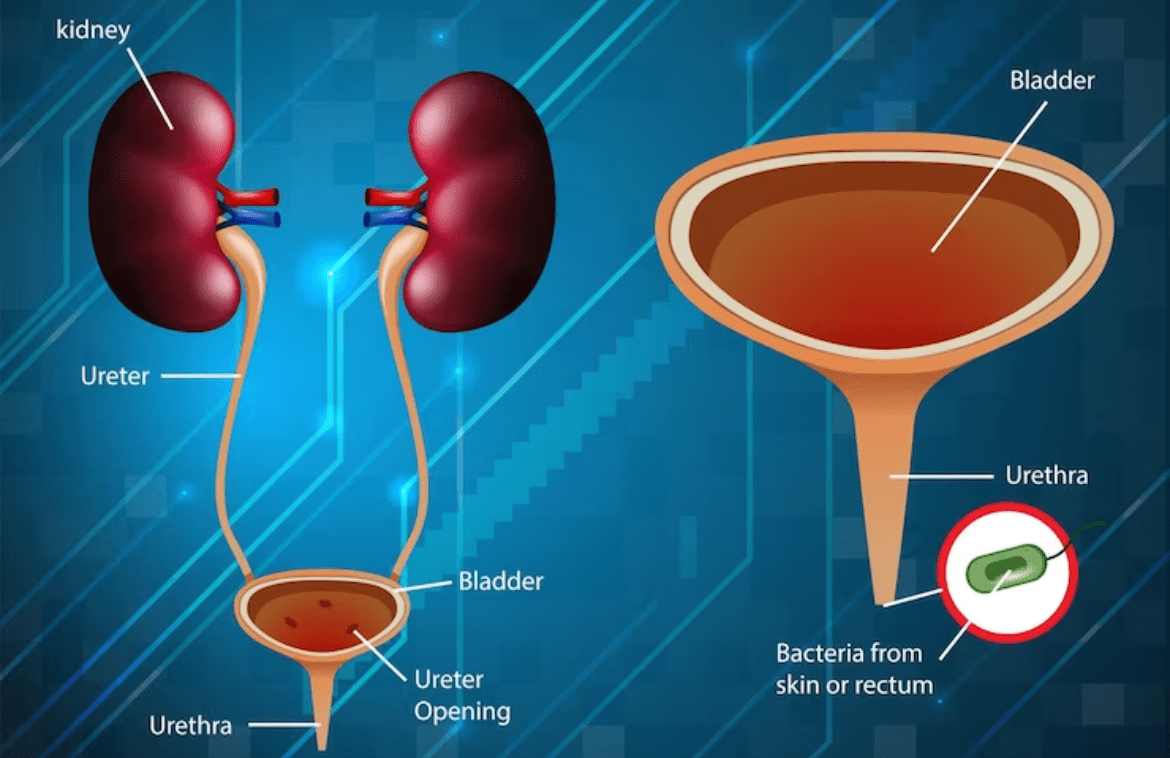
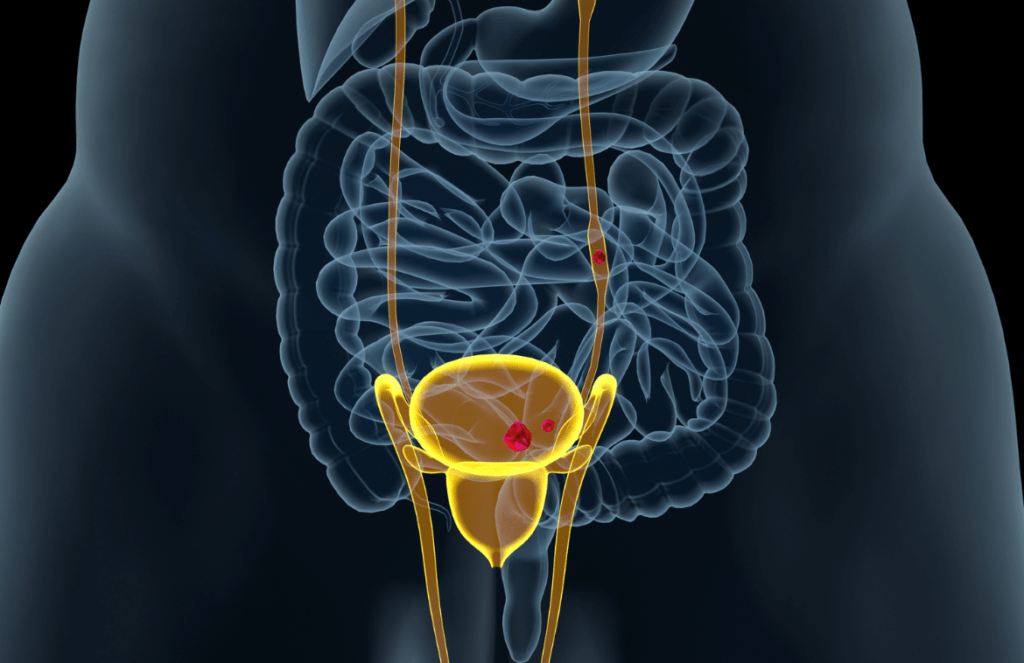
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of the urinary system. The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than men. If an infection is limited to the bladder, it can be painful and annoying. But serious health problems can result if a UTI spreads to the kidneys.
Healthcare providers often treat urinary tract infections with antibiotics. You can also take steps to lower the chance of getting a UTI in the first place.
Secrets of UTI
1. Risk factors
- Female anatomy – Women have a shorter urethra than men do.
- Sexual activity – Being sexually active tends to lead to more UTIs.
- Certain types of birth control – Using diaphragms for birth control may increase the risk of UTIs. Using spermicidal agents also can increase risk.
- Menopause – After menopause, a decline in circulating estrogen causes changes in the urinary tract which increase the risk of UTIs.
- Urinary tract problems – Babies born with problems with their urinary tracts and having problems urinating means that urine can back up in the urethra, which causes UTIs.
- Blockages in the urinary tract – Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can lead to the accumulation of urine in the bladder. Thus, the risk of UTIs is higher.
- A suppressed immune system – Diabetes as well as other diseases can indeed impair the immune system and the body’s defense against germs. This can rather increase the risk of UTIs.
- Catheter use – People who are unable to urinate on their own often require the use of a tube, known as a catheter, to urinate. Using a catheter does increase the risk of UTIs
- A recent urinary procedure – Urinary surgery or an examination of one’s urinary tract involves medical instruments which can cause a UTI.
2. Complications
When treated promptly and also properly, lower urinary tract infections do rarely lead to complications. But left untreated, UTIs can rather cause serious health problems.
- Repeated infections.
- Permanent kidney damage
- Delivering a low birth weight or premature infant.
- A narrowed urethra in men from having repeated infections of the urethra.
- Sepsis.
3. Prevention
- Drink plenty of liquids, especially water.
- Have cranberry juice.
- Wiping from front to back.
- Empty the bladder soon after having sex.
- Avoid potentially irritating feminine products.
- Change one’s birth control method.
4. Antibiotics treatment
Antibiotics are the standard treatment for UTIs because they kill the bacteria responsible for the infections. Most UTIs develop when bacteria enter the urinary tract from outside the body.
5. Causes of UTI
The organisms that tend to cause infection usually enter the urinary tract by one of two routes. The most common route is via the lower end of the urinary tract, which is the opening of a man’s urethra at the tip of the penis or even the opening of a woman’s urethra at the vulva. The infection gets down the urethra to one’s bladder, and at times to the kidneys, or even both. The other possible route does happen to be via the bloodstream, usually to the kidneys.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are also caused due to viruses. fungi, and parasites.
6. In healthy people, urine in one’s bladder is sterile—no bacteria or other infectious organisms happen to be present. The tube that does carry urine from the bladder out of one’s body (urethra) contains no bacteria or too few to cause an infection. Yet, any part of the urinary tract can become infected. Infection along the urinary tract is referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI).
Conclusion
Thus, there is much to know about UTIs.





There are no comments