Urticaria Pigmentosa Symptoms & Treatments
Urticaria pigmentosa is a skin condition that causes itching and swelling. Urticaria pigmentosa treatments are useful to get relief. It is better to avoid alcohol intake.
Urticaria pigmentosa happens to be a skin condition that is due to excess mast cells that tend to produce itching, swelling, as well as brown patches. Treatment is not usually required unless there are systemic symptoms. Yet, urticaria pigmentosa treatments can be relied upon for relief.
Discolored lesions as well as itchy skin with blisters when rubbed may indicate urticaria pigmentosa (UP). Though there is no cure, treatments ease the symptoms and discomfort that can occur due to this skin condition.
Urticaria pigmentosa (UP) happens to be an allergy-mediated skin condition that does cause discolored lesions and itchy skin. The condition reflects the presence of too many mast cells in one’s skin. Mast cells are part of one’s immune system. Their job is to produce inflammation by releasing a substance referred to as histamine in response to germs and other invaders. In UP, there are too many mast cells in one’s skin.
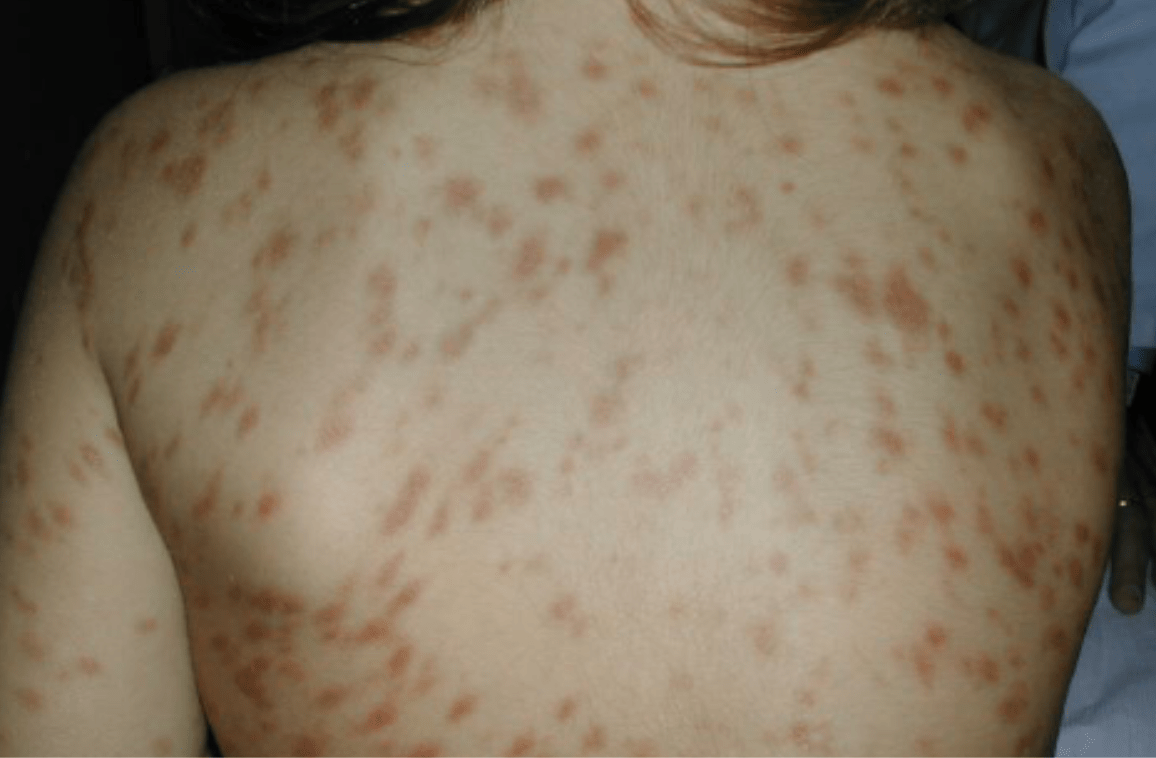
This disease is most commonly seen in infants as well as children, but it can also affect adults. The main symptom happens to be dark-colored lesions on the skin. The lesions may be very itchy and difficult not to scratch. When you rub or scratch them, the lesions do respond with a Darier’s sign. Darier’s sign does look like hives. It is due to the release of histamine from the mast cells.
In most children, UP goes away by puberty. Complications are only seen in older children or adults. Rarely, UP may evolve into systemic mastocytosis in an adult. In systemic mastocytosis, mast cells can indeed build up in other organs of one’s body. In rare cases, this may result in mast cell leukemia or even mast cell sarcoma, which are both forms of cancer.
Recognizing urticaria pigmentosa
The main symptom of UP is in the form of brownish lesions on one’s skin. Rubbing the lesions releases histamines, which do produce intense itching along with blisters or hives (Darier’s sign).
Symptoms of UP may indeed include:
- Pruritus (itching that varies in severity as well as intensity).
- Flushing (redness of one’s skin).
- Hyperpigmentation of lesions (very dark coloring of one’s lesions).
Adults or adolescents are, in fact, more likely to have uncommon symptoms. These include:
- Diarrhea.
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Fainting.
- Headache.
Treatment of urticaria pigmentosa
There is truly no cure for UP. Treatment focuses on easing symptoms and controlling lesions. The doctor will recommend a specific treatment based on the number of lesions and a person’s tolerance levels. For example, painless and easy-to-apply treatments might be best for young children.
Urticaria Pigmentosa Symptoms & Treatments
Treatment options include:
- Antihistamines are meant to relieve itching and also flush the skin.
- Topical corticosteroids (gel or perhaps cream with anti-inflammatory properties).
- Intralesional corticosteroids (injection with anti-inflammatory steroid medications).
- Hydrocolloid dressings (such as a bandage to hold medication to one’s skin).
- Fluocinolone acetonide (a synthetic corticosteroid).
- Chlorpheniramine maleate (antihistamine does control allergic reactions).
- In adults, a form of light therapy known as photo-chemotherapy using ultraviolet (UV) radiation has indeed proven to be an effective treatment.
Encouraging recovery:
- Do not rub one’s skin.
- Do not pick at the blisters (no matter how eager you may be to do so).
- Avoid scratching the lesions. This will cause more histamines, thus leading to a bigger reaction.
People suffering from UP should avoid certain medications, like:
- Aspirin
- Codeine
- Opiates (morphine and codeine)
Alcohol intake needs to be limited or eliminated since it can cause
Few possible treatments are:
- Oral antihistamines to relieve itchiness and swelling.
- Corticosteroid creams in order to reduce itching.
- Cromolyn sodium is meant to treat vomiting and diarrhea.
- Mast cell stabilizers in order to prevent mast cell activation.
- Topical steroids in order to improve skin appearance.







There are no comments