What Is Lipoma? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Lipoma cure by exercise is possible in case a patient prefers so. Lipoma attached to the muscle is possible along with other occurrences in different body parts.
A lipoma happens to be a lump of fatty tissue that does grow just under one’s skin. Most lipomas are not painful do not cause health issues and rarely need treatment. If a lipoma is bothersome, the provider can remove it or the lipoma cure by exercise is also there.
What is lipoma?
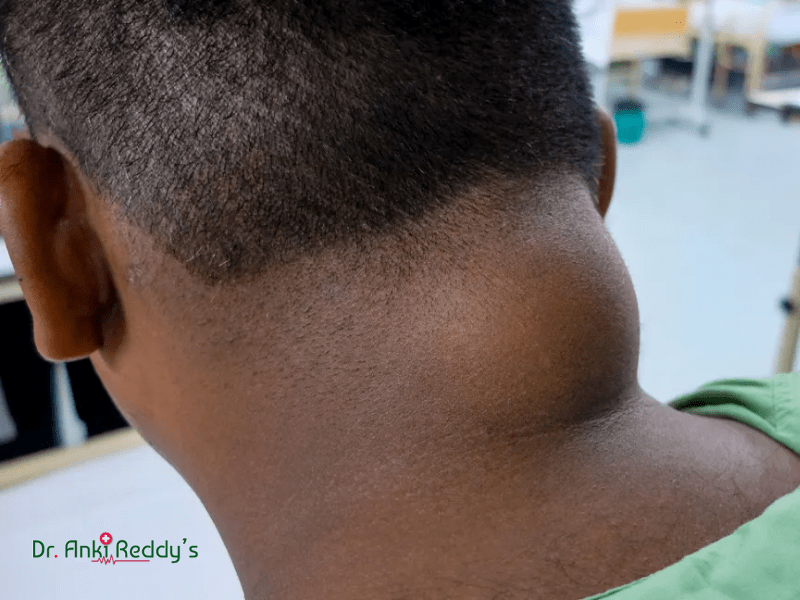
A lipoma happens to be around or oval-shaped lump of tissue that does grow just beneath the skin. It is made up of fat, moves easily when a person touches it, and does not usually cause pain. Lipomas do appear on any part of the body, but they are mostly found on the back, trunk (torso), arms, shoulders as well as neck. Also, a patient does face lipoma attached to the muscle.
Lipomas are benign soft tissue tumors. They do grow slowly and are not cancerous.
 How common are lipomas?
How common are lipomas?
Lipomas are very common and can develop at any age, even at birth. Lipomas do affect people of all genders, but they are a bit more common in women.
What are the symptoms of lipoma?
Lipomas are not usually painful but can be uncomfortable if they press against a nerve or even if they develop near a joint. Lipomas are usually:
- Encapsulated: They do not spread to the tissues surrounding them.
- Painless: Some lipomas do cause pain as well as discomfort depending on their location, size, and in case blood vessels are present.
- Round or oval-shaped: The fatty lumps of rubbery tissue are usually symmetrical.
- Moveable: They are beneath the skin’s surface and move when a person does touch them.
- Smaller than 2 inches in diameter: In a few cases, lipomas can be larger than perhaps 6 inches wide.
Where do lipomas grow?
Lipomas develop on any part of one’s body. Rarely, lipomas grow on one’s muscles, internal organs, or even the brain.
- Arms or legs.
- Back.
- Shoulders.
- Trunk (chest and torso).
- Neck.
- Forehead.
What causes lipoma?
Healthcare providers are not sure of the cause of lipomas. They are indeed inherited (passed down via families.
- Dercum’s disease: Painful lipomas develop due to this, often on a person’s arms, legs as well as trunk and is known as adiposis dolorosa or Anders’ syndrome.
- Gardner syndrome: A form of a disorder referred to as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Gardner syndrome does cause lipomas.
- Hereditary multiple lipomatosis: This is also known as familial multiple lipomatosis, this disorder is rather inherited (passed down via families).
- Madelung’s disease: This condition tends to occur most often in men who drink too much alcohol. Also referred to as multiple symmetric lipomatosis, Madelung’s disease does cause lipomas to grow around the neck as well as shoulders.
How are lipomas diagnosed?
Providers usually tend to diagnose a lipoma via a physical examination. He or she will touch the lipoma to see if it is painful or tender. A biopsy is required to confirm that the lipoma is not cancer.
Lab testing or imaging tests such as an ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, or computed tomography (CT) scan. This imaging testing help to find out if it is a lipoma versus a cyst. It also helps to identify the lipoma’s location and how deep it is if it has blood vessels as well as whether it’s pressing against nerves or other tissues.
MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT
What is the treatment for lipomas?
Most lipomas do not require treatment. If a lipoma is bothersome the provider can remove it surgically. Lipoma removal procedures are safe and also effective, and a person can usually go home on the same day.
Instead of lipoma surgery, the provider can recommend liposuction to remove the lipoma. The provider does use a long, thin needle to remove fatty tissue from the growth.
Lipoma cure by exercise is also possible.





There are no comments